Encertain: Decide Smarter
Achieve a flywheel effect in your business with an easy-to-use decision assistance tool.
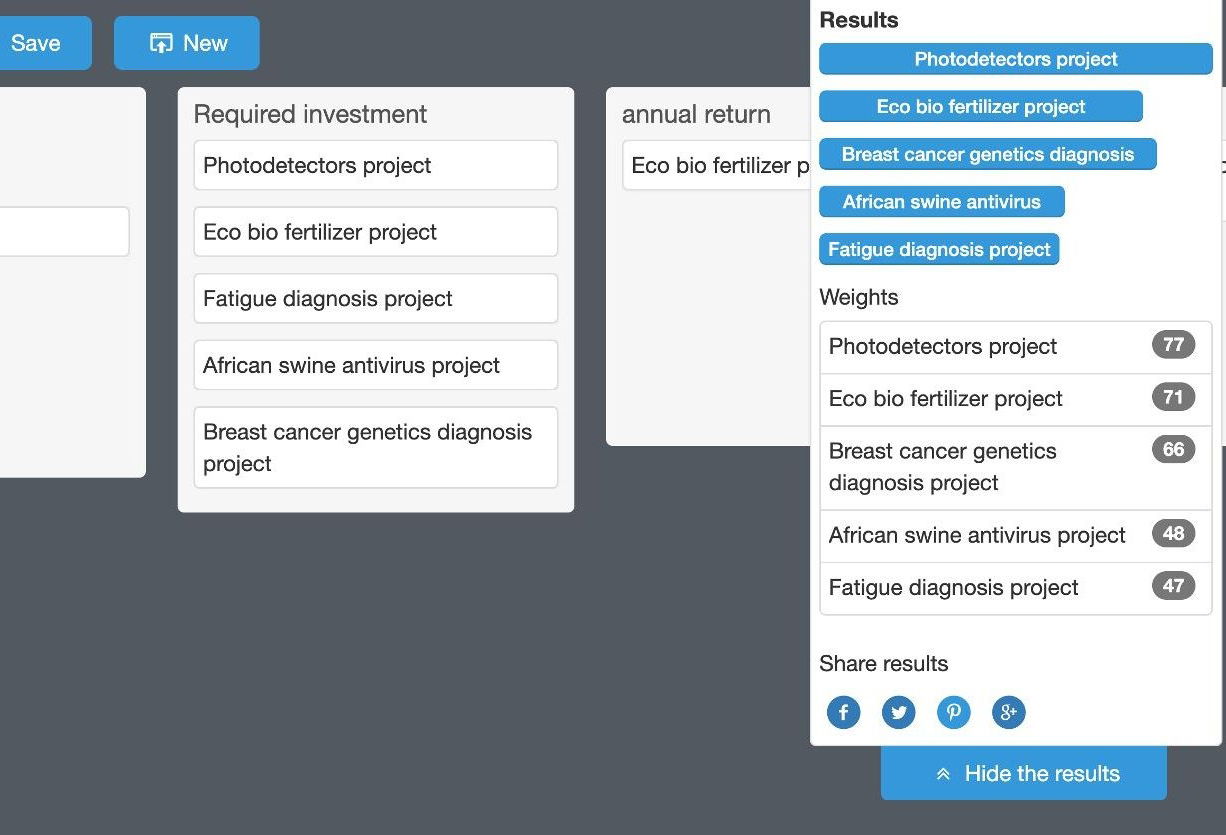

Achieve a flywheel effect in your business with an easy-to-use decision assistance tool.


Do You Have an Incentive to Make It Better?
There's a common bias that great things are costly and time-consuming, therefore it's often decided to do something satisfactory.
Whereas Pareto's principle isn't bad in some cases, the common problems with satisfactory decisions are: you prevent a flywheel effect of great decisions combined in a row, and you prevent elaborated greatness in a guaranteed way if you choose survival/satisfactory results.
Survival strategy is usually incompatible with success strategy, so in order to have great business success strategy should dominate over survival strategy.
Great things can be also quicker than good things, and not necessarily more effortful or time consuming.

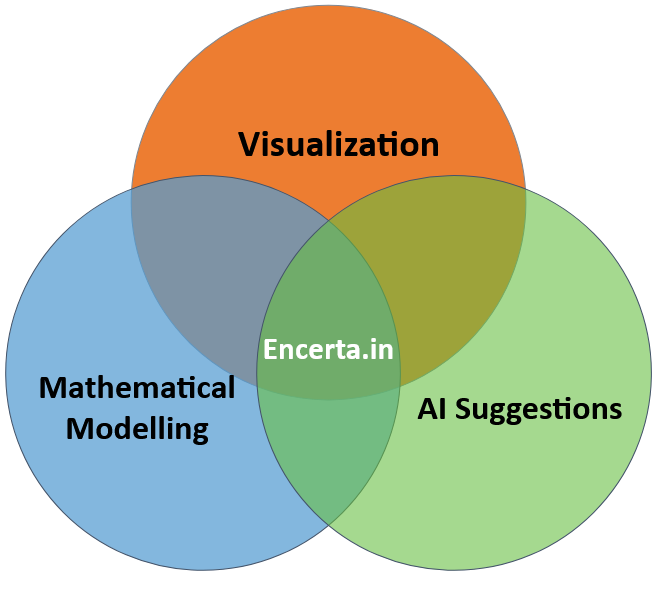
Make every time only the best (and quick) decision possible with AI-assistance and instant decision-theory-mathematical modelling.
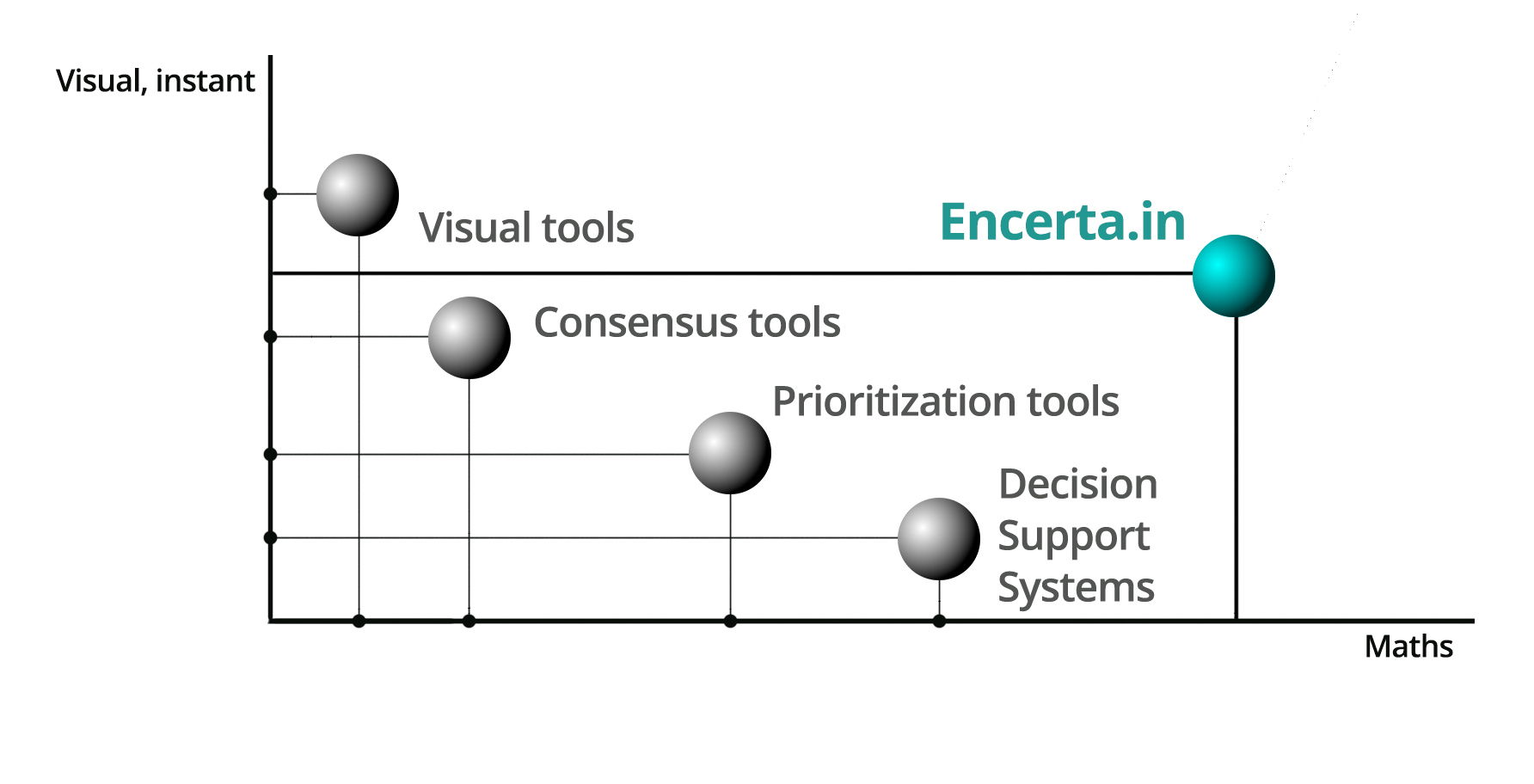
No need to master:
It's inbuilt in the software under the hood
Easy to use
Enter your alternatives and the corresponding decision factors

Prioritize your factors and move cards getting an instant math scoring

Encertain is adaptable and suitable to a high range of problems: strategic, financial, technical and many more.

Let's Work Together
We'll investigate your specific needs and decision problems.
The call will be arranged, you'll try out the software, together we'll plan the features you want and adapt the tool to your needs.
Our focus is to help you reach a quantitive-driven decisions by taking the bias out
Pricing options
The release waitlistFor those theoretically interested
$ 0 – free of charge
$ /year
|
LeanFor those wanting a simple handy facilitation tool right way
$ 100 /one off
$ /year
|
Adopters ProgramFor those having real incentive to make only great decisions
Starting at $1k/months, we'll contact you
$ 1000 /month
$ /year
|
|
|
Getting notified about the release
|
|
|
|
|
Access to the software
|
Waiting
|
|
|
|
Private consultancy
|
|
|
|
|
Integration with your software and data sources
|
|
|
|
|
Development for you
|
|
|
|
|
Customized software: Considering your needs specifically
|
|
|
|
The release waitlistFor those theoretically interested
$ 0 – free of charge
$ /year
|
|
Getting notified about the release
|
|
Access to the software
Waiting
|
|
Private consultancy
|
|
Integration with your software and data sources
|
|
Development for you
|
|
Customized software: Considering your needs specifically
|
LeanFor those wanting a simple handy facilitation tool right way
$ 100 /one off
$ /year
|
|
Getting notified about the release
|
|
Access to the software
|
|
Private consultancy
|
|
Integration with your software and data sources
|
|
Development for you
|
|
Customized software: Considering your needs specifically
|
Adopters ProgramFor those having real incentive to make only great decisions
Starting at $1k/months, we'll contact you
$ 1000 /month
$ /year
|
|
Getting notified about the release
|
|
Access to the software
|
|
Private consultancy
|
|
Integration with your software and data sources
|
|
Development for you
|
|
Customized software: Considering your needs specifically
|